Decentralized finance, or DeFi, is undoubtedly one of the most innovative applications of crypto and blockchain technology. In addition to bringing in new ways to use crypto assets, it also creates many different profit-making opportunities. One of them is yield farming. But what is yield farming, how does it work, and perhaps most importantly, how can you get the most out of it?
What Is Yield Farming? Definition
Yield farming is a strategy in the crypto markets where token holders leverage their crypto assets to earn rewards. It involves providing liquidity to decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms by lending or staking tokens in various lending protocols. This process, known as liquidity mining, helps DeFi platforms maintain liquidity and facilitate smooth transactions while giving token holders opportunities to earn passive income through the native tokens they receive as rewards.
Yield farming allows crypto investors to maximize their returns by participating in the decentralized finance ecosystem. By contributing to liquidity pools on platforms like Uniswap or Compound, they not only support the network’s functionality but also gain access to potentially high yields.
How Does Yield Farming Work?
Yield farming operates using smart contract technology, allowing investors to earn passive income from their cryptocurrency funds. It involves putting tokens and coins into decentralized applications (dApps), such as crypto wallets and decentralized exchanges (DEXs).
Yield optimization is a strategy used in yield farming to maximize returns by efficiently managing and reallocating assets across various platforms.
Investors who deposit their funds and lock them up are called liquidity providers. They are incentivized through transaction fees, interest, or income in governance tokens. Potential returns are expressed in the Annual Percentage Yield (APY) metric.
However, as more liquidity providers contribute to the liquidity pool (where assets are locked), the rewards each investor receives decrease.
Yield Farming vs. Staking
Please note that yield farmers have to deposit an equal amount of both coins/tokens in the trading pair they’re locking up.
Yield Farming Metrics
When you start researching DeFi protocols, you might run into abbreviations that you don’t recognize. Here are the 4 most common ones.
Impermanent Loss
Impermanent loss is a key risk metric in yield farming. It occurs when the value of your assets changes compared to when you deposited them. Since it can be lower when you withdraw them, this can impact your overall returns. Understanding impermanent loss is crucial for anyone involved in yield farming, as it directly affects the profitability of your investments.
Total Value Locked (TVL)
TVL, or the total value locked, is the total amount of cryptocurrency locked in a particular protocol. Usually expressed in USD, it is essentially the amount of user funds currently deposited on the DeFi platform.
Annual Percentage Yield (APY)
APY, or the annual percentage yield, is the estimated rate of return that can be gained over a period of one year on a specific investment.
Annual Percentage Rate (APR)
APR, or the annual percentage rate, is the projected rate of return on a particular investment over a period of one year. Unlike APY, it does not include compound interest.
Compounding is the act of reinvesting your gains to get bigger returns.
Types of Yield Farming
There are several ways in which you can engage in yield farming.
1. Liquidity provider
Liquidity providers are users that deposit two cryptocurrencies to a DEX to provide liquidity. Whenever somebody exchanges these two tokens or coins on a decentralized exchange, the liquidity provider gets a small cut of the transaction fee.
2. Lending
Investors can lend their tokens and coins to borrowers via smart contracts. This allows them to earn yield from the interest that borrowers pay on their loans.
3. Borrowing
Investors can lock up their funds as collateral and take a loan on another token. This borrowed token can then be used to farm yield.
4. Staking
Staking in DeFi comes in two flavors: staking on proof-of-stake blockchains that we have already mentioned above and staking the tokens you earned by depositing funds to a liquidity pool. The latter allows investors to earn yield twice.
How to Calculate Yield Farming Returns
The first thing you need to know about yield farming returns is that they’re usually annualized: this means they are calculated for a one-year period.
Yield returns are typically measured in the APR (annual percentage rate) and the APY (annual percentage yield). Please note that, unlike the latter, the former does not account for compound interest.
The APR formula is fairly simple:
APR = (Annual Return / Investment) * 100%
The APY is a little harder to calculate. First of all, you will need to know how often your interest will be compounded and how often your returns will be reinvested into the liquidity pool. Compounding interest plays a crucial role in calculating APY, as it considers the effect of reinvesting earnings over multiple periods.
Here’s the formula for it:
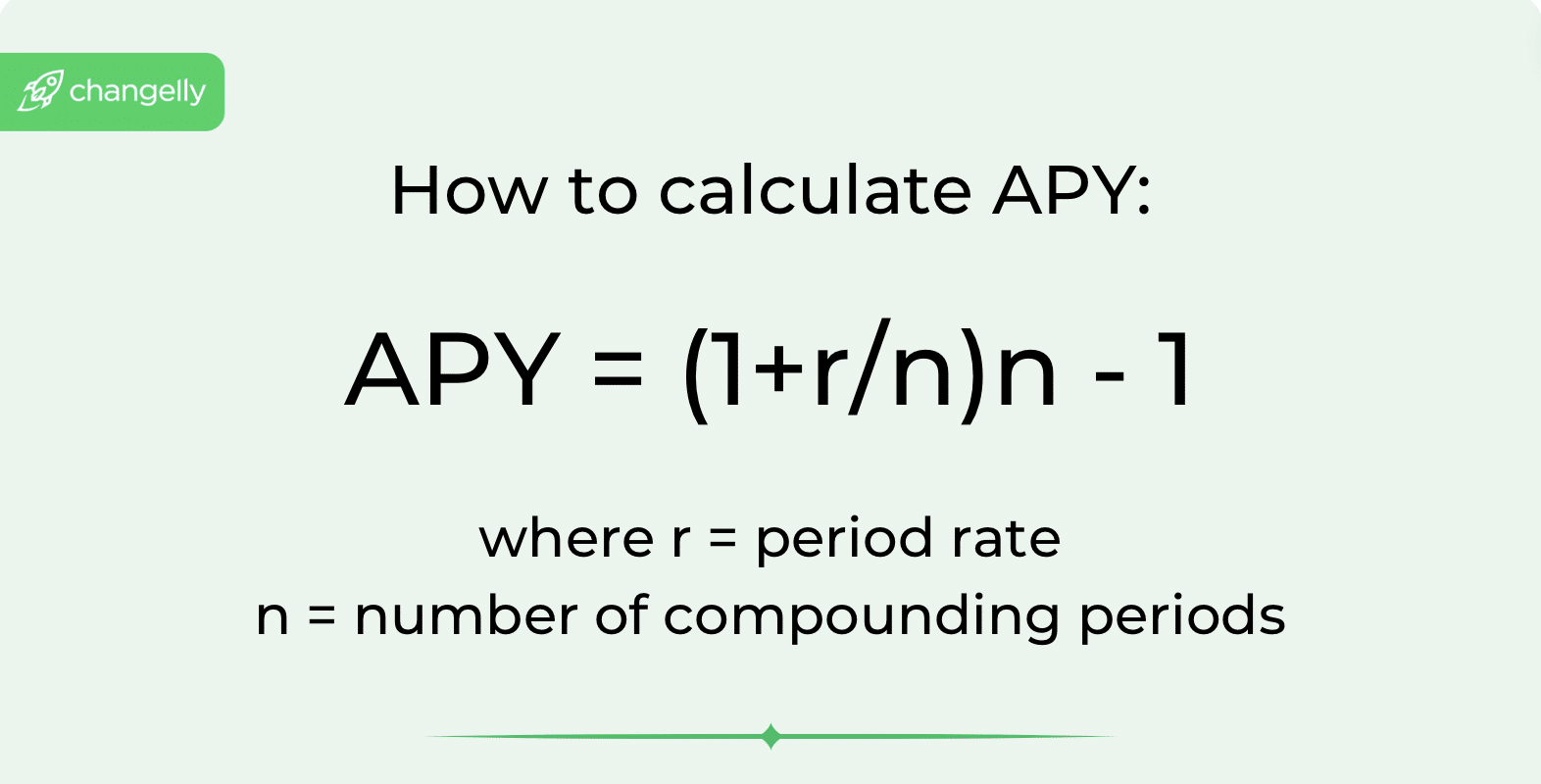
Please note that, on the whole, you won’t have to use the formula yourself because most platforms nowadays automatically calculate projected returns for you.
The Best Yield Farming Protocols
Here is a short overview of some of the biggest yield farming platforms. This section focuses on liquidity mining platforms that offer the best opportunities for making high returns.
PancakeSwap
PancakeSwap is one of the largest decentralized exchanges, operating on the Binance Smart Chain (BSC). It facilitates the swapping of BEP-20 tokens using the Automated Market Maker (AMM) model. A significant user base finds this platform attractive: it entices with lower transaction fees compared to Ethereum-based counterparts.
Aave
Aave is an open-source, non-custodial lending and borrowing protocol built on the Ethereum blockchain. It offers algorithmically adjusted yields based on supply and demand for various crypto assets supplied to the platform. Aave supports innovative features like “flash loans,” allowing borrowing and repaying within a single transaction block. The protocol also has a governance token, AAVE, which adds a layer of community-driven governance and incentives.
Uniswap
Uniswap is one of the most renowned decentralized exchanges and AMMs, known for its iconic unicorn mascot and reliability in trading ERC-20 tokens and Ethereum. On Uniswap, users can create liquidity pools for trading pairs of ETH and ERC-20 tokens. The constant product market maker mechanism adjusts the exchange rate based on liquidity changes, generating numerous trading opportunities.
Yearn Finance
Yearn Finance automatically moves user funds between various lending protocols to maximize returns. Built on Ethereum, Yearn Finance boasts a suite of products like vaults, lending, and insurance — it is only natural investors consider it a versatile platform. The protocol’s governance token, YFI, has also gained significant traction.
Balancer
Balancer is an automated portfolio manager and liquidity provider that allows users to create or join liquidity pools with multiple tokens. Flexibility and potentially higher yields go hand in hand with its dynamic fees and the ability to hold multiple tokens in customizable ratios.
Yield Farming Risks
Yield farming, while potentially highly profitable, is extremely risky. Apart from cryptocurrency price volatility, there are several other risks of yield farming investors should be wary of, including complexity and a high entry barrier in terms of knowledge and understanding of platforms. Beginners must be well-prepared and informed before diving in.
Rug Pulls
A rug pull occurs when a project’s developers abandon it and remove liquidity, leaving investors unable to sell their tokens. To avoid this, scrutinize the project’s team, reputation, tokenomics, and roadmap. Always conduct thorough research (DYOR) before investing.

Despite their reliability, smart contracts can still be hacked, posing risks to yield farmers’ investments. One specific risk factor is smart contract vulnerabilities, which can be exploited by malicious actors. Although this risk can’t be entirely avoided, researching platforms and reading reviews can help mitigate potential theft.
Regulatory Risk
The crypto industry and DeFi exist in a regulatory gray zone, with governments considering ways to regulate the market. However, DeFi’s design aims to resist regulatory pressures, suggesting limited impact from new laws.
FAQ
What are some common yield farming strategies?
Common yield farming strategies include providing liquidity to high-yield pools, staking tokens in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, and participating in liquidity mining programs. Each strategy has its own risk and reward profile, so it’s important to choose one that aligns with your investment goals.
Where can I yield farm crypto?
The most popular yield farming platforms include PancakeSwap, Uniswap, Curve Finance, Maker DAO, and more.
Is yield farming still profitable?
It can still be profitable as long as you manage your investments and risks well.
What are the benefits of yield farming?
Yield farming offers the potential to generate yields that can exceed traditional financial instruments, scoring attractive returns on digital assets. Additionally, it rewards participants with extra tokens, enhancing overall profitability within the DeFi ecosystem.
Who are yield farmers?
Yield farmers are individuals or entities that participate in the yield farming process by contributing liquidity to decentralized exchanges or other DeFi protocols. They aim to generate yields and earn additional rewards from their investments in the DeFi ecosystem and by benefitting from market volatility.
What is a liquidity pool?
A liquidity pool is a collection of digital assets locked in a smart contract on a decentralized exchange to facilitate trading and lending. Liquidity pools infuse necessary liquidity to enable smooth transactions and market operations. No surprise they’re essential to the yield farming process.
Who are liquidity providers?
Liquidity providers are individuals or entities that supply digital assets to liquidity pools on decentralized exchanges. By contributing liquidity, they help maintain market stability and are rewarded with yield farming rewards, earning additional returns for their participation in the DeFi yield farming ecosystem.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.
Decentralized finance, or DeFi, is undoubtedly one of the most innovative applications of crypto and blockchain technology. In addition to bringing in new ways to use crypto assets, it also creates many different profit-making opportunities. One of them is yield farming. But what is yield farming, how does it work, and perhaps most importantly, how can you get the most out of it?
What Is Yield Farming? Definition
Yield farming is a strategy in the crypto markets where token holders leverage their crypto assets to earn rewards. It involves providing liquidity to decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms by lending or staking tokens in various lending protocols. This process, known as liquidity mining, helps DeFi platforms maintain liquidity and facilitate smooth transactions while giving token holders opportunities to earn passive income through the native tokens they receive as rewards.
Yield farming allows crypto investors to maximize their returns by participating in the decentralized finance ecosystem. By contributing to liquidity pools on platforms like Uniswap or Compound, they not only support the network’s functionality but also gain access to potentially high yields.
How Does Yield Farming Work?
Yield farming operates using smart contract technology, allowing investors to earn passive income from their cryptocurrency funds. It involves putting tokens and coins into decentralized applications (dApps), such as crypto wallets and decentralized exchanges (DEXs).
Yield optimization is a strategy used in yield farming to maximize returns by efficiently managing and reallocating assets across various platforms.
Investors who deposit their funds and lock them up are called liquidity providers. They are incentivized through transaction fees, interest, or income in governance tokens. Potential returns are expressed in the Annual Percentage Yield (APY) metric.
However, as more liquidity providers contribute to the liquidity pool (where assets are locked), the rewards each investor receives decrease.
Yield Farming vs. Staking
Please note that yield farmers have to deposit an equal amount of both coins/tokens in the trading pair they’re locking up.
Yield Farming Metrics
When you start researching DeFi protocols, you might run into abbreviations that you don’t recognize. Here are the 4 most common ones.
Impermanent Loss
Impermanent loss is a key risk metric in yield farming. It occurs when the value of your assets changes compared to when you deposited them. Since it can be lower when you withdraw them, this can impact your overall returns. Understanding impermanent loss is crucial for anyone involved in yield farming, as it directly affects the profitability of your investments.
Total Value Locked (TVL)
TVL, or the total value locked, is the total amount of cryptocurrency locked in a particular protocol. Usually expressed in USD, it is essentially the amount of user funds currently deposited on the DeFi platform.
Annual Percentage Yield (APY)
APY, or the annual percentage yield, is the estimated rate of return that can be gained over a period of one year on a specific investment.
Annual Percentage Rate (APR)
APR, or the annual percentage rate, is the projected rate of return on a particular investment over a period of one year. Unlike APY, it does not include compound interest.
Compounding is the act of reinvesting your gains to get bigger returns.
Types of Yield Farming
There are several ways in which you can engage in yield farming.
1. Liquidity provider
Liquidity providers are users that deposit two cryptocurrencies to a DEX to provide liquidity. Whenever somebody exchanges these two tokens or coins on a decentralized exchange, the liquidity provider gets a small cut of the transaction fee.
2. Lending
Investors can lend their tokens and coins to borrowers via smart contracts. This allows them to earn yield from the interest that borrowers pay on their loans.
3. Borrowing
Investors can lock up their funds as collateral and take a loan on another token. This borrowed token can then be used to farm yield.
4. Staking
Staking in DeFi comes in two flavors: staking on proof-of-stake blockchains that we have already mentioned above and staking the tokens you earned by depositing funds to a liquidity pool. The latter allows investors to earn yield twice.
How to Calculate Yield Farming Returns
The first thing you need to know about yield farming returns is that they’re usually annualized: this means they are calculated for a one-year period.
Yield returns are typically measured in the APR (annual percentage rate) and the APY (annual percentage yield). Please note that, unlike the latter, the former does not account for compound interest.
The APR formula is fairly simple:
APR = (Annual Return / Investment) * 100%
The APY is a little harder to calculate. First of all, you will need to know how often your interest will be compounded and how often your returns will be reinvested into the liquidity pool. Compounding interest plays a crucial role in calculating APY, as it considers the effect of reinvesting earnings over multiple periods.
Here’s the formula for it:

Please note that, on the whole, you won’t have to use the formula yourself because most platforms nowadays automatically calculate projected returns for you.
The Best Yield Farming Protocols
Here is a short overview of some of the biggest yield farming platforms. This section focuses on liquidity mining platforms that offer the best opportunities for making high returns.
PancakeSwap
PancakeSwap is one of the largest decentralized exchanges, operating on the Binance Smart Chain (BSC). It facilitates the swapping of BEP-20 tokens using the Automated Market Maker (AMM) model. A significant user base finds this platform attractive: it entices with lower transaction fees compared to Ethereum-based counterparts.
Aave
Aave is an open-source, non-custodial lending and borrowing protocol built on the Ethereum blockchain. It offers algorithmically adjusted yields based on supply and demand for various crypto assets supplied to the platform. Aave supports innovative features like “flash loans,” allowing borrowing and repaying within a single transaction block. The protocol also has a governance token, AAVE, which adds a layer of community-driven governance and incentives.
Uniswap
Uniswap is one of the most renowned decentralized exchanges and AMMs, known for its iconic unicorn mascot and reliability in trading ERC-20 tokens and Ethereum. On Uniswap, users can create liquidity pools for trading pairs of ETH and ERC-20 tokens. The constant product market maker mechanism adjusts the exchange rate based on liquidity changes, generating numerous trading opportunities.
Yearn Finance
Yearn Finance automatically moves user funds between various lending protocols to maximize returns. Built on Ethereum, Yearn Finance boasts a suite of products like vaults, lending, and insurance — it is only natural investors consider it a versatile platform. The protocol’s governance token, YFI, has also gained significant traction.
Balancer
Balancer is an automated portfolio manager and liquidity provider that allows users to create or join liquidity pools with multiple tokens. Flexibility and potentially higher yields go hand in hand with its dynamic fees and the ability to hold multiple tokens in customizable ratios.
Yield Farming Risks
Yield farming, while potentially highly profitable, is extremely risky. Apart from cryptocurrency price volatility, there are several other risks of yield farming investors should be wary of, including complexity and a high entry barrier in terms of knowledge and understanding of platforms. Beginners must be well-prepared and informed before diving in.
Rug Pulls
A rug pull occurs when a project’s developers abandon it and remove liquidity, leaving investors unable to sell their tokens. To avoid this, scrutinize the project’s team, reputation, tokenomics, and roadmap. Always conduct thorough research (DYOR) before investing.

Despite their reliability, smart contracts can still be hacked, posing risks to yield farmers’ investments. One specific risk factor is smart contract vulnerabilities, which can be exploited by malicious actors. Although this risk can’t be entirely avoided, researching platforms and reading reviews can help mitigate potential theft.
Regulatory Risk
The crypto industry and DeFi exist in a regulatory gray zone, with governments considering ways to regulate the market. However, DeFi’s design aims to resist regulatory pressures, suggesting limited impact from new laws.
FAQ
What are some common yield farming strategies?
Common yield farming strategies include providing liquidity to high-yield pools, staking tokens in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, and participating in liquidity mining programs. Each strategy has its own risk and reward profile, so it’s important to choose one that aligns with your investment goals.
Where can I yield farm crypto?
The most popular yield farming platforms include PancakeSwap, Uniswap, Curve Finance, Maker DAO, and more.
Is yield farming still profitable?
It can still be profitable as long as you manage your investments and risks well.
What are the benefits of yield farming?
Yield farming offers the potential to generate yields that can exceed traditional financial instruments, scoring attractive returns on digital assets. Additionally, it rewards participants with extra tokens, enhancing overall profitability within the DeFi ecosystem.
Who are yield farmers?
Yield farmers are individuals or entities that participate in the yield farming process by contributing liquidity to decentralized exchanges or other DeFi protocols. They aim to generate yields and earn additional rewards from their investments in the DeFi ecosystem and by benefitting from market volatility.
What is a liquidity pool?
A liquidity pool is a collection of digital assets locked in a smart contract on a decentralized exchange to facilitate trading and lending. Liquidity pools infuse necessary liquidity to enable smooth transactions and market operations. No surprise they’re essential to the yield farming process.
Who are liquidity providers?
Liquidity providers are individuals or entities that supply digital assets to liquidity pools on decentralized exchanges. By contributing liquidity, they help maintain market stability and are rewarded with yield farming rewards, earning additional returns for their participation in the DeFi yield farming ecosystem.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.




















































































I’m extremely inspired with your writing abilities as smartly as with the layout for your weblog. Is that this a paid theme or did you modify it yourself? Anyway keep up the nice quality writing, it’s rare to see a nice blog like this one these days!
cost of cheap clomid pills can you get clomid for sale buying generic clomid pill how to buy clomid tablets where to get cheap clomiphene tablets how to get clomiphene without dr prescription cost of clomid no prescription
Facts blog you procure here.. It’s intricate to on high worth writing like yours these days. I honestly appreciate individuals like you! Take vigilance!!
More peace pieces like this would make the интернет better.
buy zithromax tablets – tinidazole 500mg uk order flagyl 400mg generic
buy rybelsus generic – order cyproheptadine 4 mg generic buy generic cyproheptadine online
motilium tablet – order cyclobenzaprine 15mg for sale cyclobenzaprine 15mg us
order inderal 10mg pills – inderal 10mg tablet buy methotrexate online
generic esomeprazole 20mg – https://anexamate.com/ buy nexium 40mg generic
order coumadin 2mg generic – blood thinner losartan cost
buy generic mobic – https://moboxsin.com/ meloxicam 7.5mg tablet
deltasone oral – allergic reactions generic prednisone 5mg
amoxicillin cost – buy generic amoxicillin cheap generic amoxil
cheap diflucan 200mg – https://gpdifluca.com/# buy generic diflucan for sale
order cenforce without prescription – https://cenforcers.com/ buy cenforce cheap
cialis medicine – tadalafil buy online canada what is the normal dose of cialis
zantac cheap – https://aranitidine.com/# buy zantac 300mg sale
cialis male enhancement – cialis for daily use reviews tadalafil medication
More articles like this would remedy the blogosphere richer. este sitio
viagra sale lloyds pharmacy – https://strongvpls.com/ viagra 50mg price
This website exceedingly has all of the tidings and facts I needed about this thesis and didn’t positive who to ask. https://ursxdol.com/augmentin-amoxiclav-pill/
This is the type of enter I turn up helpful. https://buyfastonl.com/gabapentin.html
This is the type of delivery I unearth helpful. https://prohnrg.com/product/priligy-dapoxetine-pills/
More posts like this would make the blogosphere more useful. https://ondactone.com/spironolactone/
This website really has all of the bumf and facts I needed there this participant and didn’t identify who to ask.
https://doxycyclinege.com/pro/meloxicam/
Good blog you have here.. It’s obdurate to find great status belles-lettres like yours these days. I really respect individuals like you! Take vigilance!! https://sportavesti.ru/forums/users/esmfb-2/