- Ethereum gas fees has fallen below $100,000.
- The total supply of ETH has increased in the last few months.
Ethereum [ETH], once notorious for its significantly high gas fees, has recently seen a massive decline in transaction costs.
While this reduction in fees has made the network more accessible and affordable for users, it has also sparked concerns about the potential impact on ETH value.
Ethereum gas fees hit five-year lows
A report from Kaiko, dated the 19th of August, revealed that Ethereum’s gas fees have plummeted to five-year lows.
This development is driven by increased activity on Layer 2 solutions and the impact of the Dencun upgrade in March 2024.
This upgrade notably lowered transaction fees on Layer 2 networks, contributing to the decline in overall gas fees.
According to Dune Analytics, March 2024 was the last time Ethereum’s gas fees saw a significant spike, reaching over $603.2 million.
Since then, fees have steadily declined, with July 2024 recording fees of around $93.4 million. Kaiko’s research suggests that the current month is on track to see the lowest fees.
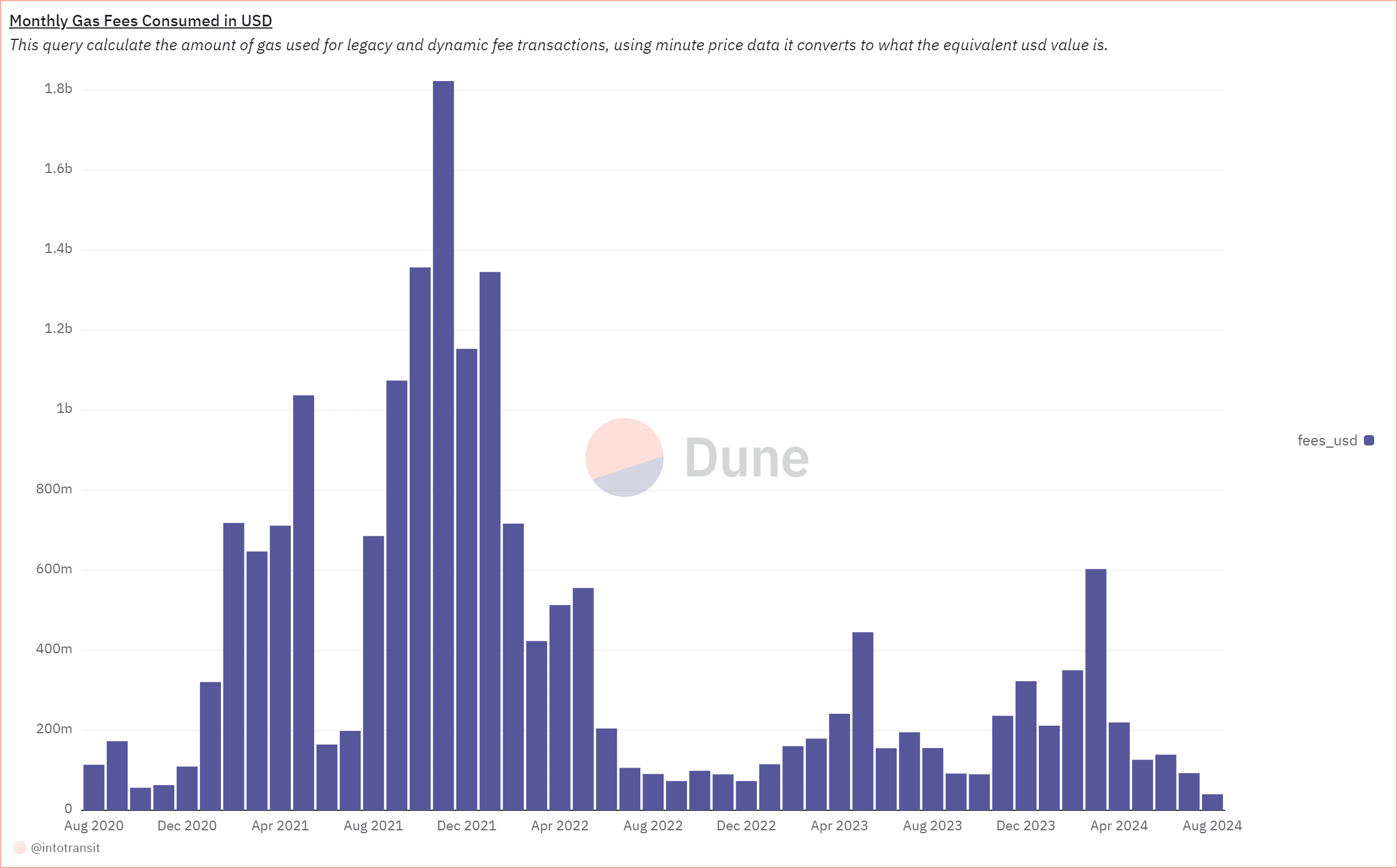
Source: DuneAnalytics
One important consequence of lower gas fees is the reduction in the amount of ETH being burned. Under Ethereum’s EIP-1559 mechanism, a portion of gas fees is burned, effectively reducing the supply of ETH.
With lower fees, less ETH is being burned, potentially leading to an increase in the token’s supply over time.
Supply increase
The reduction in Ethereum gas fees, largely driven by the Dencun upgrade and increased Layer 2 activity, has led to a decrease in the amount of ETH burned through transaction fees.
Consequently, the total supply of ETH has gradually increased from 120 million in March 2024 to over 120.2 million currently. This trend has been gradual but consistent, as evidenced by data from Glassnode.
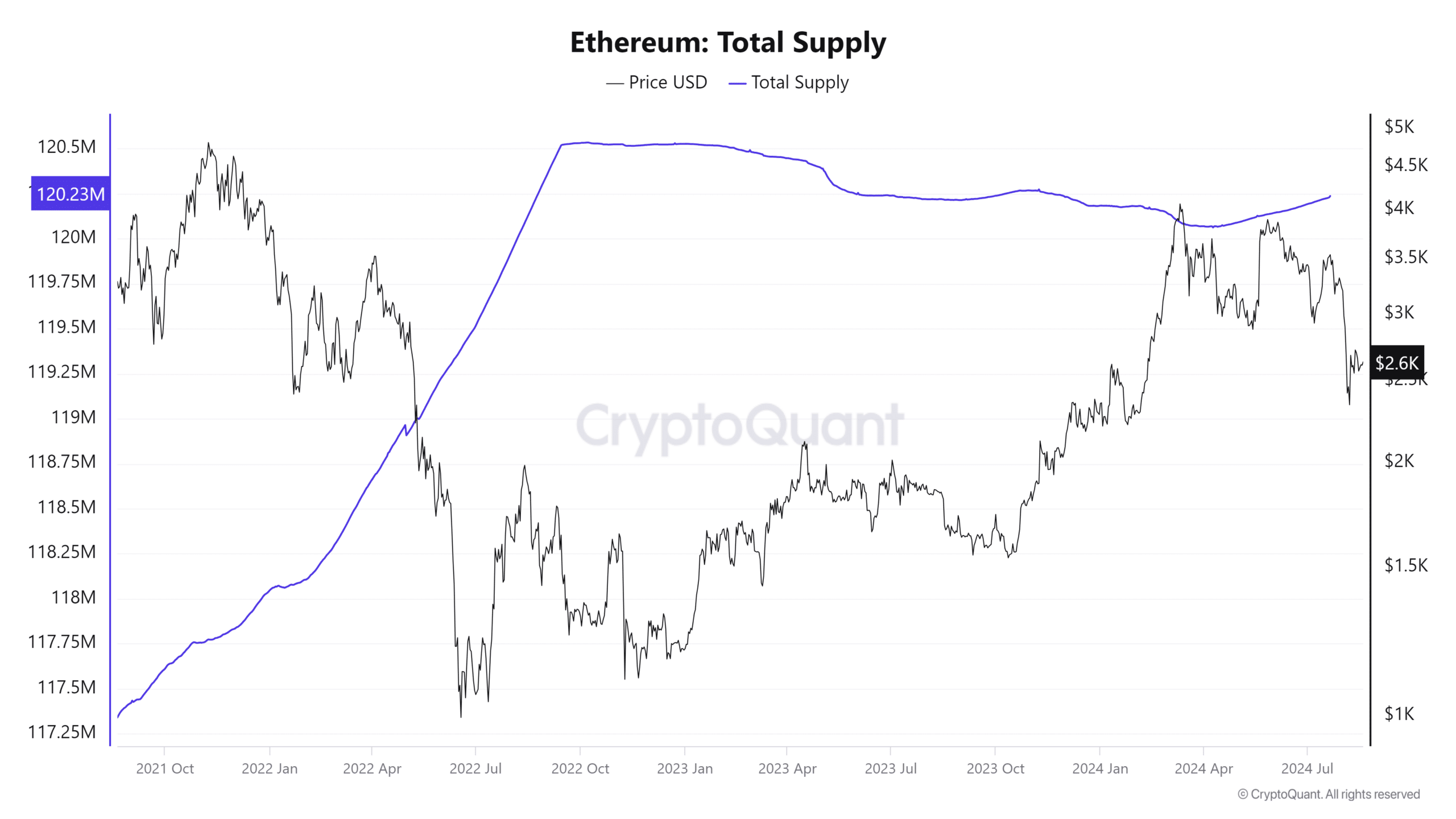
Source: CryptoQuant
Kaiko’s report highlighted that this growing supply of ETH could temper potential price increases in the near term, even in the face of positive demand drivers such as spot ETH ETFs.
The increase in supply, without a corresponding surge in demand, could exert downward pressure on ETH prices.
ETH remains in a bear trend
AMBCrypto’s look at Ethereum’s price trend revealed that the $3,000 level has recently become a significant psychological resistance point.
As of this writing, Ethereum is trading at approximately $2,648, showing a slight increase of less than 1%.
Is your portfolio green? Check out the ETH Profit Calculator
Despite this modest gain, Ethereum has struggled to approach or test the $3,000 resistance level, with its short-moving average (yellow line) acting as a formidable barrier.
Furthermore, the Relative Strength Index (RSI) for Ethereum was around 40 at press time, indicating that the market was in a strong bearish trend.
- Ethereum gas fees has fallen below $100,000.
- The total supply of ETH has increased in the last few months.
Ethereum [ETH], once notorious for its significantly high gas fees, has recently seen a massive decline in transaction costs.
While this reduction in fees has made the network more accessible and affordable for users, it has also sparked concerns about the potential impact on ETH value.
Ethereum gas fees hit five-year lows
A report from Kaiko, dated the 19th of August, revealed that Ethereum’s gas fees have plummeted to five-year lows.
This development is driven by increased activity on Layer 2 solutions and the impact of the Dencun upgrade in March 2024.
This upgrade notably lowered transaction fees on Layer 2 networks, contributing to the decline in overall gas fees.
According to Dune Analytics, March 2024 was the last time Ethereum’s gas fees saw a significant spike, reaching over $603.2 million.
Since then, fees have steadily declined, with July 2024 recording fees of around $93.4 million. Kaiko’s research suggests that the current month is on track to see the lowest fees.

Source: DuneAnalytics
One important consequence of lower gas fees is the reduction in the amount of ETH being burned. Under Ethereum’s EIP-1559 mechanism, a portion of gas fees is burned, effectively reducing the supply of ETH.
With lower fees, less ETH is being burned, potentially leading to an increase in the token’s supply over time.
Supply increase
The reduction in Ethereum gas fees, largely driven by the Dencun upgrade and increased Layer 2 activity, has led to a decrease in the amount of ETH burned through transaction fees.
Consequently, the total supply of ETH has gradually increased from 120 million in March 2024 to over 120.2 million currently. This trend has been gradual but consistent, as evidenced by data from Glassnode.

Source: CryptoQuant
Kaiko’s report highlighted that this growing supply of ETH could temper potential price increases in the near term, even in the face of positive demand drivers such as spot ETH ETFs.
The increase in supply, without a corresponding surge in demand, could exert downward pressure on ETH prices.
ETH remains in a bear trend
AMBCrypto’s look at Ethereum’s price trend revealed that the $3,000 level has recently become a significant psychological resistance point.
As of this writing, Ethereum is trading at approximately $2,648, showing a slight increase of less than 1%.
Is your portfolio green? Check out the ETH Profit Calculator
Despite this modest gain, Ethereum has struggled to approach or test the $3,000 resistance level, with its short-moving average (yellow line) acting as a formidable barrier.
Furthermore, the Relative Strength Index (RSI) for Ethereum was around 40 at press time, indicating that the market was in a strong bearish trend.


















































































where can i get generic clomiphene without dr prescription good rx clomid can i buy cheap clomiphene without prescription can you buy clomid for sale how to get cheap clomid price can i get clomiphene prices cost of clomid pill
I’ll certainly bring back to skim more.
Thanks on sharing. It’s acme quality.
cheap zithromax 500mg – azithromycin 250mg drug brand flagyl 200mg
buy rybelsus 14 mg – order cyproheptadine 4 mg generic cost periactin 4 mg
motilium where to buy – motilium online buy buy cyclobenzaprine
buy cheap inderal – methotrexate 10mg cheap order methotrexate 10mg for sale
amoxil order – amoxicillin where to buy combivent 100 mcg ca
augmentin without prescription – atbioinfo.com purchase ampicillin pill
order nexium pill – https://anexamate.com/ order generic esomeprazole 40mg
buy coumadin without prescription – https://coumamide.com/ losartan cost
purchase mobic online – swelling mobic 7.5mg tablet
prednisone 5mg pills – https://apreplson.com/ buy generic deltasone 10mg
cheap erectile dysfunction pills online – https://fastedtotake.com/ buy erectile dysfunction medication
purchase amoxicillin without prescription – amoxil over the counter purchase amoxicillin
purchase diflucan pill – https://gpdifluca.com/ purchase fluconazole online cheap
cenforce order – https://cenforcers.com/# cenforce brand
generic cialis super active tadalafil 20mg – https://ciltadgn.com/# cialis 20mg tablets
buy cialis without doctor prescription – on this site how long does it take for cialis to take effect
buy ranitidine 150mg – click buy zantac generic
50 mg viagra cost – https://strongvpls.com/ 50 or 100mg viagra
I’ll certainly carry back to skim more. este sitio
I couldn’t hold back commenting. Adequately written! https://buyfastonl.com/
Thanks on putting this up. It’s understandably done. https://ursxdol.com/furosemide-diuretic/
This is a theme which is forthcoming to my verve… Many thanks! Exactly where can I upon the connection details an eye to questions? https://prohnrg.com/product/loratadine-10-mg-tablets/
More posts like this would make the blogosphere more useful. https://aranitidine.com/fr/prednisolone-achat-en-ligne/
More content pieces like this would insinuate the интернет better. https://ondactone.com/simvastatin/